Computer Science/Data Structure
[자료구조] 배열(Array)(2): 프로그래밍 언어는 배열을 어떻게 구현했을까? (in Java, Python, C++)
깃짱
2023. 12. 7. 10:00
반응형
반응형
Computer Science 모아보기 👉🏻 https://github.com/seoul-developer/CS
GitHub - seoul-developer/CS: 주니어 개발자를 위한 전공 지식 모음.zip
주니어 개발자를 위한 전공 지식 모음.zip. Contribute to seoul-developer/CS development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
💋 프로그래밍 언어에서의 배열 사용해보기
✔️ C++
int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; //Static Integer Array
int *a = new int[5]; //Dynamic Integer Array
✔️ Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Static Array
int[] staticArray = new int[5];
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// Dynamic Array
// Create an ArrayList of integers.
ArrayList<Integer> dynamicArray = new ArrayList<>();
// Add elements to the dynamic array.
dynamicArray.add(1);
dynamicArray.add(2);
dynamicArray.add(3);
// Remove an element from the dynamic array.
dynamicArray.remove(1);
}
}
나는 메인 언어가 자바인 개발자이므로, 자바에서 구현한 동적 배열인 ArrayList에 대해서만 추가적으로 설명을 이어보도록 하겠습니다. 아래에서는 비슷한 느낌으로다가 구현 코드도 넣었으니 참고해주세요.
- 데이터 추가 (
add()) add()메서드를 사용하여 요소를 배열의 끝에 추가할 수 있다.- 메모리 동작: 만약 내부 배열이 가득 차 있으면, 현재 크기의 약 1.5배 정도의 새로운 배열을 할당하고 이전 배열의 요소들을 새 배열로 복사합니다. 그 후 새로운 요소가 추가됩니다.
- 데이터 삭제 (
remove) remove메서드를 사용하여 특정 인덱스의 요소를 삭제할 수 있습니다.- 메모리 동작: 삭제된 요소 뒤에 있는 모든 요소들을 한 칸씩 앞으로 이동시켜 공간을 메웁니다. 만약 이로 인해 배열의 사용된 크기가 일정 비율 이하로 떨어진다면,
shrinkSize()메서드로 내부 배열의 크기를 줄일 수 있습니다. - 데이터 변경 (
set) set메서드를 사용하여 특정 인덱스의 요소를 변경할 수 있습니다.- 메모리 동작: 해당 인덱스의 요소만 변경되며, 배열의 크기나 메모리 할당에는 영향을 미치지 않습니다.
- shrinkSize()
- 사용자가 직접 호출하여 내부 배열의 크기를 현재 요소의 개수에 맞게 조절할 수 있습니다.
- 메모리 동작: 현재 요소의 개수에 맞게 크기가 조절되며, 불필요한 메모리가 해제됩니다.
- Iterator 사용
Iterator를 사용하여 배열의 요소를 순회할 수 있습니다.- 메모리 동작: 별도의 메모리 할당 없이 배열의 원소에 직접 접근합니다.
✔️ Python
# Static List
a_static = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Dynamic List (equivalent to dynamic array in some contexts)
a_dynamic = [0] * 5 # Initialize with zeros, similar to new int[5] in C++
# Alternatively, you can use the list() constructor to create a dynamic list
a_dynamic_alternative = list(range(5))
# Print the lists
print("Static List:", a_static)
print("Dynamic List:", a_dynamic)
print("Dynamic List (alternative):", a_dynamic_alternative)
# Coded By Block_Cipher
💋 자바로 ArrayList 간단하게 구현해보기
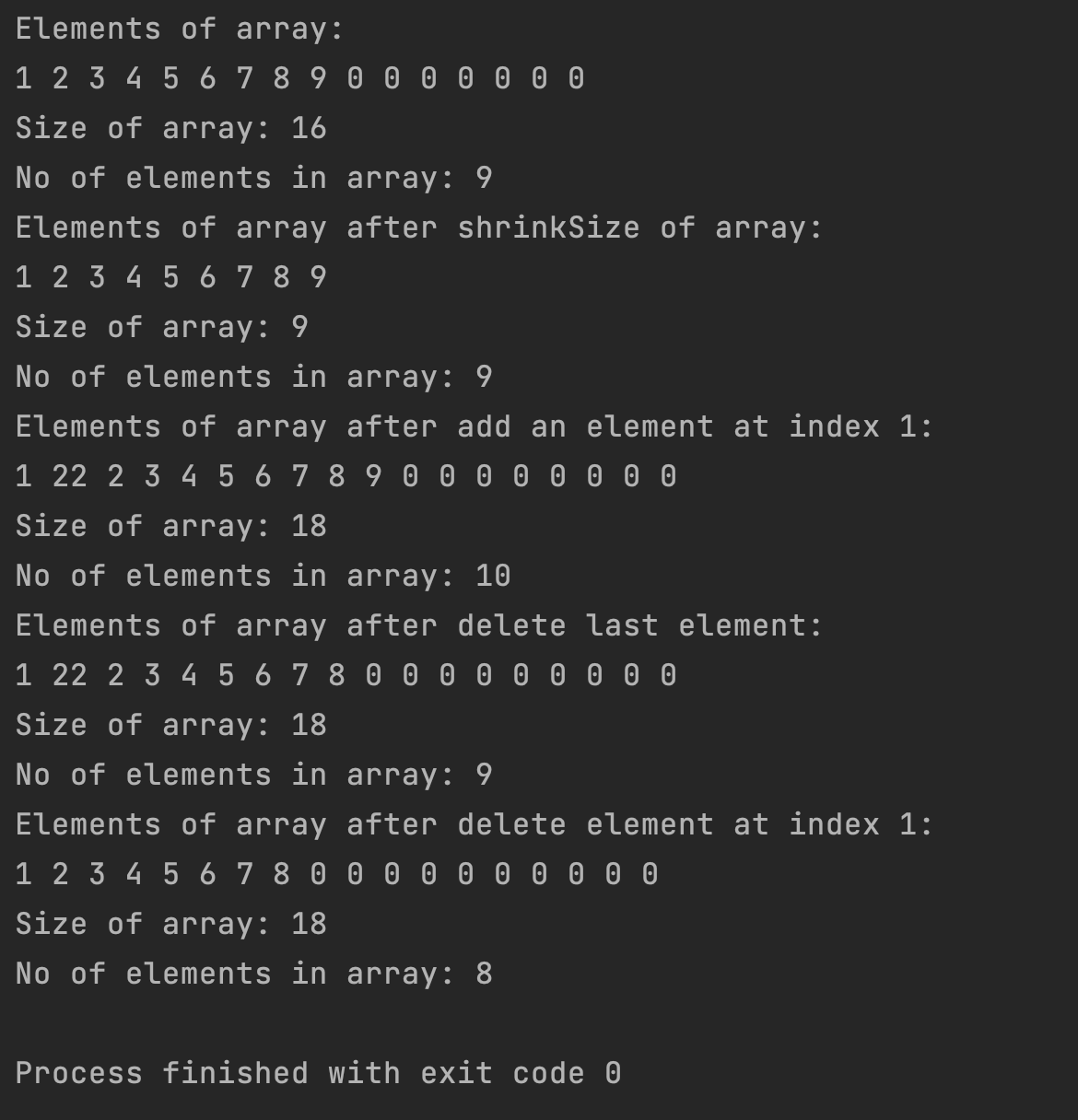
결과는 아래에!
// Java program deals with all operation of a dynamic array
// add, remove, resize memory of array is the main feature
public class DynamicArray {
// create three variable array[] is a array,
// count will deal with no of element add by you and
// size will with size of array[]
private int array[];
private int count;
private int size;
// constructor initialize value to variable
public DynamicArray() {
array = new int[1];
count = 0;
size = 1;
}
// function add an element at the end of array
public void add(int data) {
// check no of element is equal to size of array
if (count == size) {
growSize(); // make array size double
} // insert element at end of array
array[count] = data;
count++;
}
// function makes size double of array
public void growSize() {
int temp[] = null;
if (count == size) {
// temp is a double size array of array
// and store array elements
temp = new int[size * 2];
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// copy all array value into temp
temp[i] = array[i];
}
}
}
// double size array temp initialize
// into variable array again
array = temp;
// and make size is double also of array
size = size * 2;
}
// function shrink size of array
// which block unnecessary remove them
public void shrinkSize() {
int temp[] = null;
if (count > 0) {
// temp is a count size array
// and store array elements
temp = new int[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// copy all array value into temp
temp[i] = array[i];
}
size = count;
// count size array temp initialize
// into variable array again
array = temp;
}
}
// function add an element at given index
public void addAt(int index, int data) {
// if size is not enough make size double
if (count == size) {
growSize();
}
for (int i = count - 1; i >= index; i--) {
// shift all element right
// from given index
array[i + 1] = array[i];
}
// insert data at given index
array[index] = data;
count++;
}
// function remove last element or put
// zero at last index
public void remove() {
if (count > 0) {
array[count - 1] = 0;
count--;
}
}
// function shift all element of right
// side from given index in left
public void removeAt(int index) {
if (count > 0) {
for (int i = index; i < count - 1; i++) {
// shift all element of right
// side from given index in left
array[i] = array[i + 1];
}
array[count - 1] = 0;
count--;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DynamicArray da = new DynamicArray();
// add 9 elements in array
da.add(1); // Size of array: 1
da.add(2); // Size of array: 2
da.add(3); // Size of array: 4
da.add(4); // Size of array: 4
da.add(5); // Size of array: 8
da.add(6); // Size of array: 8
da.add(7); // Size of array: 8
da.add(8); // Size of array: 8
da.add(9); // Size of array: 16
// print all array elements after add 9 elements
System.out.println("Elements of array:");
for (int i = 0; i < da.size; i++) {
System.out.print(da.array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// print size of array and no of element
System.out.println("Size of array: " + da.size);
System.out.println("No of elements in array: "
+ da.count);
// shrinkSize of array
da.shrinkSize();
// print all array elements
System.out.println("Elements of array after shrinkSize of array:");
for (int i = 0; i < da.size; i++) {
System.out.print(da.array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// print size of array and no of element
System.out.println("Size of array: " + da.size);
System.out.println("No of elements in array: "
+ da.count);
// add an element at index 1
da.addAt(1, 22); // Size of array: 18
// print Elements of array after adding an
// element at index 1
System.out.println("Elements of array after add an element at index 1:");
for (int i = 0; i < da.size; i++) {
System.out.print(da.array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// print size of array and no of element
System.out.println("Size of array: " + da.size);
System.out.println("No of elements in array: " + da.count);
// delete last element
da.remove();
// print Elements of array after delete last
// element
System.out.println("Elements of array after delete last element:");
for (int i = 0; i < da.size; i++) {
System.out.print(da.array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// print size of array and no of element
System.out.println("Size of array: " + da.size);
System.out.println("No of elements in array: " + da.count);
// delete element at index 1
da.removeAt(1);
// print Elements of array after delete
// an element index 1
System.out.println("Elements of array after delete element at index 1:");
for (int i = 0; i < da.size; i++) {
System.out.print(da.array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// print size of array and no of element
System.out.println("Size of array: " + da.size);
System.out.println("No of elements in array: "
+ da.count);
}
}
💋 참고자료

도움이 되었다면, 공감/댓글을 달아주면 깃짱에게 큰 힘이 됩니다!🌟
비밀댓글과 메일을 통해 오는 개인적인 질문은 받지 않고 있습니다. 꼭 공개댓글로 남겨주세요!
반응형